Product Description
Gear refers to a mechanical component with teeth on the rim that can continuously mesh to transmit motion and power. The application of gears in transmission appeared very early. At the end of the 19th century, the principle of developing the cutting method and the special machine tools and tools using this principle appeared 1 after another, and with the development of production, the smoothness of gear operation was paid attention to.
CHINAMFG MACHINERY CO., LTD is 1 professional and excellent Corporation engaged in designing and producing machinery and materials for the field of Prestressed Concrete Industry and Post Tensioning Industry in construction and argriculture field in China, which is a manufacture and an international trading enterprise.
The company established in year 2008, under the guidance of reform and opening-up policy and with the help of government at all levels, with all of our staffs hardworking, has continuously developed at steady speed. At present, Our company has a total staff of 60, a workshop area of 2400m2, mechanical equipment manufacturing base at HangZhou. The company,with stable strength advantages in the brand, quality, technology, market, scale and benefit, has been making contribution to the local economic development.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
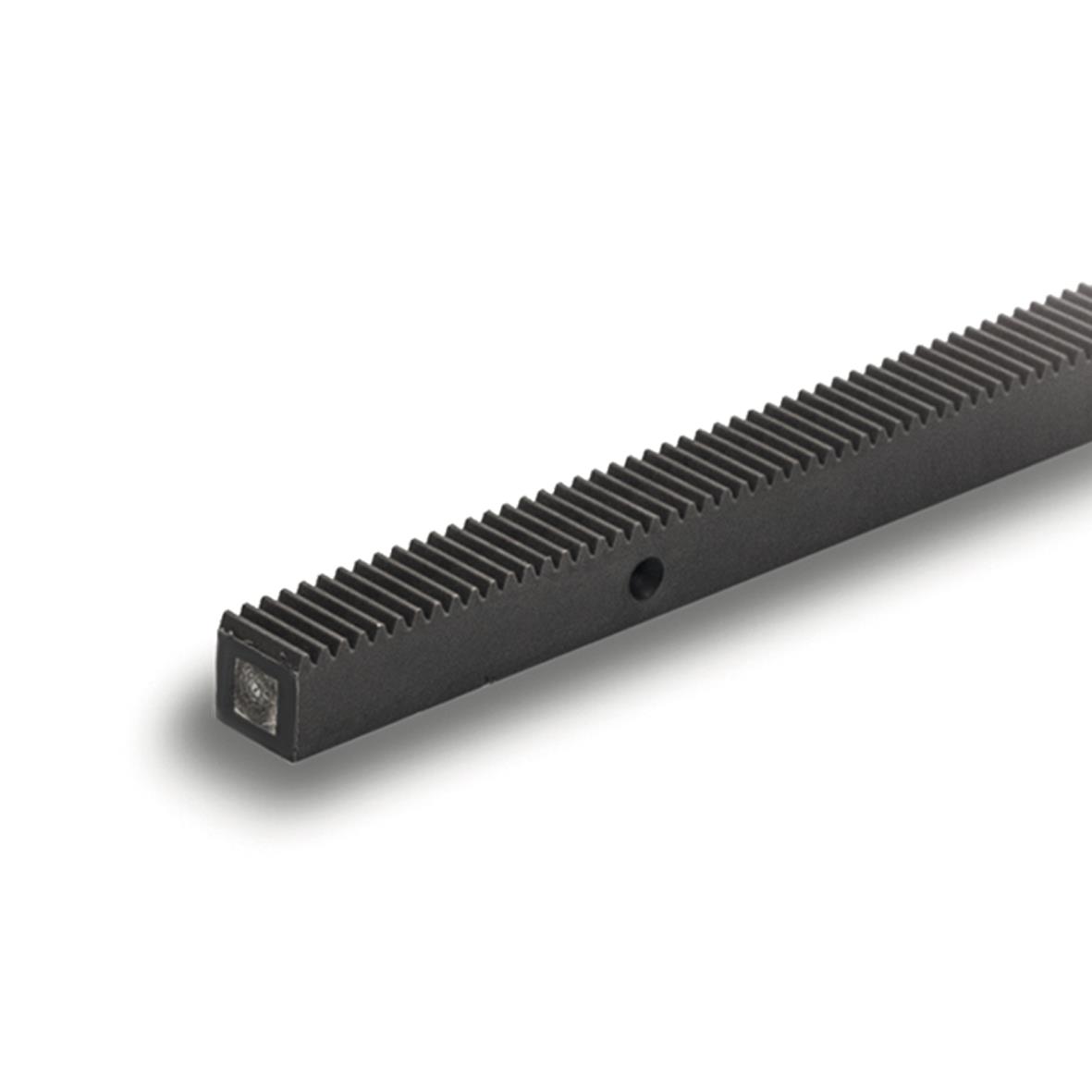

How do rack and pinion systems handle variations in load capacity and speed?
Rack and pinion systems are designed to handle variations in load capacity and speed effectively. Here’s a detailed explanation of how they handle these variations:
- Load Capacity: Rack and pinion systems can be designed to accommodate a wide range of load capacities. The load capacity primarily depends on the strength and size of the rack and pinion components, such as the rack material, tooth size, and pinion gear dimensions. By selecting appropriate materials and dimensions, rack and pinion systems can be optimized to handle varying load capacities. For higher load requirements, heavier-duty materials and larger gear sizes can be used to ensure sufficient strength and durability.
- Speed: Rack and pinion systems can also handle variations in speed. The speed of the system is influenced by factors such as the rotational speed of the pinion gear and the pitch of the rack. By adjusting these parameters, the speed of the system can be optimized to suit specific application requirements. For high-speed applications, rack and pinion systems can be designed with smaller pitch and lighter components to minimize inertia and allow for rapid acceleration and deceleration. On the other hand, for slower-speed applications, larger pitch and heavier components can be used to enhance stability and load-carrying capacity.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of rack and pinion systems. Lubricants help reduce friction and wear between the rack and pinion gears, ensuring efficient power transmission and minimizing the risk of damage. The type and frequency of lubrication required may vary depending on the load capacity and speed of the system. Regular maintenance, including inspection and lubrication, is important to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the rack and pinion system under varying load and speed conditions.
- Design Considerations: When designing rack and pinion systems, it is essential to consider the anticipated load capacity and speed requirements. Factors such as gear material selection, tooth profile, gear module, and tooth width play a significant role in determining the system’s ability to handle variations in load and speed. The design should take into account the maximum expected load and speed to ensure that the rack and pinion components are appropriately sized and capable of withstanding the anticipated conditions.
- System Feedback and Control: In applications where load and speed variations are significant, incorporating system feedback and control mechanisms can enhance the performance of rack and pinion systems. Sensors and feedback devices can be used to monitor the load and speed, allowing for real-time adjustments and control. This feedback information can be utilized to implement closed-loop control systems that adjust the motor torque or speed to maintain precise motion control under varying load conditions.
By considering factors such as load capacity, speed, lubrication, maintenance, and design considerations, rack and pinion systems can effectively handle variations in load and speed, ensuring reliable and precise motion control in a wide range of applications.
How do rack and pinion systems handle variations in backlash and precision?
Rack and pinion systems are designed to minimize variations in backlash and ensure high precision in motion control. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rack and pinion systems handle variations in backlash and precision:
Backlash in Rack and Pinion Systems:
Backlash refers to the play or clearance between the teeth of the pinion and the rack in a rack and pinion system. It can result in a loss of precision and accuracy in motion control. However, there are several strategies employed to handle variations in backlash:
- Precision Manufacturing: Rack and pinion systems are manufactured with high precision to minimize backlash. The teeth of both the pinion and the rack are carefully machined to ensure accurate tooth profiles and proper tooth engagement. Precision manufacturing techniques, such as grinding and honing, are utilized to achieve tight tolerances and reduce backlash to a minimum.
- Preload Mechanisms: Preload mechanisms can be incorporated into rack and pinion systems to reduce or eliminate backlash. These mechanisms apply a slight force or tension to the pinion and the rack, ensuring constant contact between the teeth. By eliminating the clearance between the teeth, preload mechanisms minimize backlash and enhance precision. Common preload mechanisms include spring-loaded systems, adjustable shims, and anti-backlash devices.
- Compensation Techniques: Compensation techniques can be employed to handle variations in backlash. These techniques involve implementing controls or software algorithms that account for the expected backlash and compensate for it during motion control. By applying appropriate corrections and adjustments, the system can achieve the desired precision and accuracy, even in the presence of backlash.
Precision in Rack and Pinion Systems:
Precision in rack and pinion systems refers to the ability to achieve accurate and repeatable motion control. Several factors contribute to maintaining precision in rack and pinion systems:
- Rigidity and Structural Integrity: The rigidity and structural integrity of the rack and pinion system play a crucial role in maintaining precision. Stiffness in the system ensures minimal deflection or deformation during operation, allowing for accurate positioning and motion control. Proper selection of materials, adequate sizing of components, and robust construction are essential for maintaining precision.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is important for reducing friction and wear in rack and pinion systems. Adequate lubrication minimizes variations in friction, ensuring smooth and consistent motion. Regular maintenance, including lubrication checks and cleaning, helps to preserve precision over time and prevent degradation in performance.
- System Alignment: Precise alignment of the rack and pinion system is critical for maintaining precision. Proper alignment ensures accurate tooth engagement and minimizes variations in backlash. Alignment procedures may involve careful adjustment of mounting positions, gear meshing, and system calibration to achieve optimal precision.
By employing precision manufacturing techniques, incorporating preload mechanisms, utilizing compensation techniques, ensuring system rigidity, implementing effective lubrication and maintenance practices, and maintaining proper system alignment, rack and pinion systems can handle variations in backlash and maintain high precision in motion control. These measures contribute to accurate positioning, repeatability, and reliable performance in a wide range of applications.

What are the primary components of a rack and pinion setup?
In a rack and pinion setup, there are two primary components that make up the mechanism: the rack and the pinion gear. Here’s a detailed explanation of each component:
- Rack: The rack is a straight bar with teeth cut along its length. It resembles a gear but in a linear form. The rack is typically a long, narrow strip made of metal or a durable engineering plastic. The teeth on the rack are evenly spaced and have a specific profile that allows them to mesh with the teeth on the pinion gear. The rack can be stationary, meaning it remains fixed in place, or it can move linearly in response to the rotational motion of the pinion gear.
- Pinion Gear: The pinion gear is a small circular gear with teeth that mesh with the teeth on the rack. It is usually mounted on a rotating shaft, such as a motor shaft or an actuator. When rotational force is applied to the pinion gear, it rotates, causing the teeth on the pinion to engage with the teeth on the rack. The pinion gear transfers its rotational motion to the rack, resulting in linear motion. The size and design of the pinion gear, including the number and shape of its teeth, are chosen based on the specific application requirements.
Together, the rack and pinion gear form a mechanical linkage that converts rotational motion into linear motion. As the pinion gear rotates, its teeth push against the teeth on the rack, causing the rack to move linearly. This linear motion can be harnessed for various applications, such as steering systems, robotic arms, linear actuators, and other mechanisms that require controlled linear movement.
In summary, the rack and pinion setup consists of a rack, a straight bar with teeth, and a pinion gear, a small circular gear. These two components work together to enable the conversion of rotational motion into linear motion, offering a versatile and efficient solution for various mechanical systems.


editor by Dream 2024-04-26